About Guar
Guar also known as cluster bean (Cyamopsis tetragonolobus (L.) Taub), a drought hardy leguminous crop. Guar is being grown for seed, green fodder, vegetable and green manuring. It is an annual plant, about 4 feet high, vertically stalked, with large leaves and clusters of pods. Each pod is about 5-8 cm long and has on an average 6-9 small grayish-white pea shaped seeds. The pods are used as a green vegetable or as a cattle feed besides the industrial extraction of guar gum. Guar grows best in sandy soils. It needs moderate, intermittent rainfall with lots of sunshine. The crop is sown after the first rains in July and harvested in October-November. It is a short duration crop and is harvested within 3-4 months of its plantation. Guar is a rain dependent crop; rainfall influences the yield of the crop. Its seed consists of seed coat, endosperm and germ. It has attained an important place in industry because of its galactomannan rich endosperm (splits).

Guar Plant

Guar Pods

Guar Seeds

Guar Endosperm

Guar Gum Powder
Processing of Guar Seeds to make Guar Splits: The gum is commercially extracted from the seeds essentially by a mechanical process of roasting, differential attrition, sieving and polishing. The seeds are broken and the germ is separated from the endosperm. Two halves of the endosperm are obtained from each seed and are known as undehusked guar splits. When the fine layer of fibrous material, which forms the husk, is removed and separated from the endosperm halves by polishing, guar splits are obtained and the yield of the same is ranging from 27-29%. The hull (husk) and germ portion of guar seed are termed as guar meal (guar protein) and the yield of the same is ranging from 70-72%.
Processing of Guar Splits to make Guar Gum Powder: The guar splits are made refined by sieving and sorting processes. Refined guar splits are then treated and finished into powders (known as guar gum) by a variety of routes and processing techniques depending upon the end product desired. The basic process included hydration of refined guar splits, flaking, grinding drying followed by sieving and packing.
Guar Gum Powder: It is a galactomannan polysaccharide, has a chain of (1→4)-linked-β-D-mannopyranosyl units with single α-D-galactopyranosyl units connected by (1→6) linkages to, on the average, every second main chain unit.
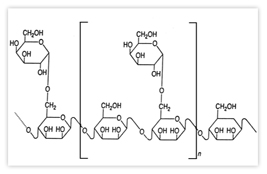
Structure of Guar Galactomannan



